نوع مقاله : Supplement
نویسندگان
1 استاد گروه زراعت و اصلاح نباتات، دانشگاه فردوسی مشهد
2 استاد گروه اقتصاد کشاورزی، دانشگاه فردوسی مشهد
3 مدیر داخلی نشریات علمی پژوهشی دانشگاه تربت حیدریه
4 کارشناس نشریات علمی پژوهشی دنشگاه تربت حیدریه
5 مدیر گروه تولیدات گیاهی، دانشگاه تربت حیدریه
6 مدیر گروه اقتصاد کشاورزی، دانشگاه تربت حیدریه
کلیدواژهها
عنوان مقاله [English]
Saffron Agronomy and Technology (Book of Abstracts: 2013-2016)
نویسندگان [English]
- Parviz Rezvani Moghaddam 1
- Alireza Karbasi 2
- Moein Tosan 3
- Faezeh Gharari 4
- Hassan Feizi 5
- Toktam Mohtashami 6
1 Professor, Faculty of Agriculture, Ferdowsi University of Mashhad
2 Professor, Faculty of Agriculture, Ferdowsi University of Mashhad
3 Journals Executive Director, University of Torbat Heydarieh.
4 Journals Expert, University of Torbat Heydarieh
5 University of Torbat Heydarieh
6 University of Torbat Heydarieh
چکیده [English]
Khorasan province in Iran with a diverse climatic conditions has accommodated a wide range of plant communities particularly herbs, spices and medicinal plants. Among these Saffron (Crocus sativus L.), has been the most cultivated plant for thousands of years. These crop deliver unique interests and applications. The novel use of Saffron in recent years in cancer cure have been promenaded and stimulated more investigation on this crop. Almost 94% of the total world’s Saffron production (298 t) and 95% of the total Iran’s Saffron production (280 t) originates from Khorasan province. Saffron is unique for the area where water scarcity is the most limiting factor in crop productions for the farmer. Saffron is almost cultivated and harvested and also to some extent processed by family workers and community cooperation bases. These crop is not only the most important source of income for farmers but also historically strong socio-cultural activities have been formed within the local community. Cultivation area and its surrounding environment conditions and production volume of Saffron, has made Khorasan province a unique location in the world. The sustainable management of these traditionally cultivated and used plants not only helps to conserve nationally and globally important biodiversity but also provides critical resources to sustain livelihoods.
کلیدواژهها [English]
- Abstracts
- Book
- Saffron
Journal Info:
Saffron Agronomy and Technology is a peer review and open access journal publish by university of Torbat Heydarieh and Saffron Institute with associate Iranian Medicinal Plant Society as quarterly (4 issues per year). The research papers of different fields of Saffron science, e.g. Agriculture, basic science, medical properties, biotechnology, genetic and plant breeding, processing, food industry, phytochemical properties, economic, marketing and other related subjects to Saffron are published in this journal for dissemination of the scientific knowledge and research. Journal of Saffron Agronomy and Technology is basically dedicated to promoting scholarly exchanges among professors, researchers, and students of different universities, and research institutes, focusing in particular on the exploration of cutting edge knowledge on Saffron science and technology. A digital object identifier (DOI) is a type of persistent identifier used to uniquely identify objects. The DOI system is particularly used for electronic documents such as journal articles.
Peer Review Processing
All new submissions are screened for completeness and adherence to the Guide for Authors. Those that pass are then assigned to a Senior Editor for consideration for sending for peer review. Authors of manuscripts rejected at initial evaluation stage will normally be informed within 1-2 week of receipt.
Torbat Heydarieh
Torbat Heydarieh is a city in the Khorasan Razavi Province, northeast of Iran. Torbat Heydarieh city is 1005 km. far from Tehran and is located in a mountainous region on the skirt of mountain having different weathers in different areas. The name Torbat in Persian means Burial place, thus the name of the city means Burial Place of Heydar named after Qotboddin whose tomb lies in the heart of the city.
Saffron Institute
Saffron research institute of Torbat Heydarieh University is one of the first specialized institute of Saffron in Iran and the world. This institute was established with aims to educate and promote fundamental researches related to Saffron, in 2007.
Chapter 1- Agronomy
Iran has a long history of saffron production and has a lot of established saffron populations which are being cultivated since ancient times. Saffron in the Islamic Republic of Iran is planted as a perennial crop, and its cultivated area has increased greatly from 4100 ha in 1981 to 61775 ha in 2012. Producing more than 90% of the global production of saffron, Iran is certainly the most important saffron producing country in the world. Khorasan Razavi province, with 61775 ha of saffron fields, is the greatest saffron cultivation area in Iran. In this province, saffron production creates a very key income for numerous rural families and is an important source of employment. One of the most important saffron production and cultivation regions in this province is Torbat Heydarieh covering about 45.5% (28100 ha) of the cultivated area in Khorasan Razavi province in 2012. In Iran, cultivation of saffron is important from different aspects including high water productivity, employment, and non-oil exports. Currently, this product provides a major part of the income of rural families in the Razavi and Southern Khorasan provinces. In terms of employment, it creates around 270 person day work per a growing season. Currently, the global production of saffron is 330 ton per year where Iran with a production of 310 ton annually has the first rank in the world and has claimed over 94% of the global production of this product. Production of saffron in five countries including Spain, Greece, Morocco, India, and China, standing in the next ranks after Iran, is a trivial amount in total where their production does not exceed even 20 ton.
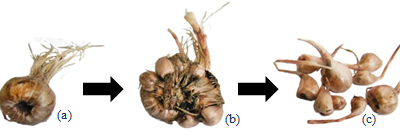
Production Stages of replacement corms (Koocheki et al., 2014).
(a) Mother corm in planting time, (b) Mother corm in end of the first growing season, (c) Nine replacement corms of saffron.
Chapter 2-Basic Sciences
The red stigmas constitute the most important economic portion of saffron flower. This part of the flower contains carbohydrates, minerals, vitamins, and some kind of pigments including carotene and flavones. Although saffron is mainly used as a coloring, flavoring, and fragrance condiment for a variety of foods, existence of special chemical compounds in it have made it a suitable candidate to be used in pharmaceuticals as well. The saffron color, bitter taste, and scent are due to crocin, picrocrocin (HC626O7), and safranal (C10H14O), respectively. Among the major ingredients of saffron, crocetin, which is responsible for its coloring property, is a special carotenoid with multi-unsaturated conjugate olefin acid structure. The compound exhibits favorable effects in the prevention or treatment of a variety of diseases such as dyslipidemia, atherosclerosis, myocardial ischemia, hemorrhagic shock, cancer and arthritis. Crocetin also showed obvious inhibitory effects on atherogenic factor-induced disorders in vascular endothelial cells, smooth muscle cells and monocyte-derived macrophages.
Chapter 3-Breeding and Genetic Study
Saffron (Crocus sativus L.) is a sterile autumn-flowering species, which propagates vegetatively by means of a tuberous bulb, known as a corm. Genetic improvement and propagation of high quality plant material could improve saffron industrialization and stop the process of genetic erosion. A high quality and improved plant is supposed to produce more flowers per plant, flowers with a higher number of stigmas, increasing stigma sizes or stigmas with an increased amount of dye and aroma.

Different reaction of various explants to tissue culture in different hormonal media (Sajjadi F ard and Pazhouhandeh, 2015).
Chapter 4-Economics
Saffron has a specific economic value for farmers in Khorasan Province in terms of revenue and job generation. This commodity ranks second in export of agricultural product for the country. Economic value of Saffron could be observed during the flower picking period where almost all business in the area including transport are highly involved.
Marketing routes Saffron Khorasan Razavi (Shaban et al., 2015).
Chapter 5- Medical
Saffron has been known since Antiquity as a remedy for all pains, without claiming to be a universal medicine, it is however a natural solution for many health problems in our times. Traditional knowledge can be used as a source for development of new medicines. A variety of properties of saffron including diuretic, analgesic, anti-inflammatory, hepatoprotective, appetite suppressant, hypnotic, antidepressant, and bronchodilator effects may forms some of these medical fields of study.
A summary of cardiovascular effects of saffron (Razavi et al., 2015).
Chapter 6- Meteorology
Climate is one of the most important and effective factors in Saffron cultivation. Corm sprouting, flower initiation and time of flowering are the critical stages that are influenced by environmental fluctuations in terms of temperature and availability of water. Any change in the critical limit of climate conditions influences the growth of the saffron plant and finally the production of economic product. This make it necessery to study on the effects of climate change on saffron.
The actual zonation based on average of saffron yield during 20 years (Tosan et al., 2015).

